Introduction
The Lienhuachih Forest Dynamics Plot (FDP) is the second 25-ha permanent plot in Taiwan. It is located in the 4th and 6th Forest Compartments of the Lienhuachih Experimental Forest (LEF) in central Taiwan (23º54’49”N, 120º52’43”E). The topography of the plot is characterized by hills with valleys, steep slopes, and ridges. The average slope of plots is about 35.3°, so the land is very steep. Topographic features display high spatial heterogeneity within the plot.
The climatic characteristics of this area are hot summers with warm winters, and the range of average monthly temperatures is small throughout the year. Moreover, it has a distinct dry season. The mean annual temperature is 20.8°C. The mean relative humidity is 87.1%. The annual precipitation is 2285.0 mm with seasonality. More than half of the rain falls between May and September (about 89.6% of the total rainfall). In terms of natural disturbances, on average, 0.7 typhoons pass by the area each year and often cause severe damage. Typhoons usually bring extremely heavy rainfall and result in over-saturation of soil water. Because of the steep slopes in this area, typhoons often cause serious landslides, which in turn influence the forest structure and biodiversity.
Following the FDP methodology developed by the Center for Tropical Forest Science, we set up this plot with a projected area of 25 ha. The plot is square in shape, measuring 500 m (north-south) by 500 m (east-west). The elevation of the plot ranges from 667 m to 845 m a.s.l. In the 25-ha plot, we identified, measured, tagged, and mapped every shrub and tree with diameter at breast height (DBH) of ≥ 1 cm.
In total, 153,268 (6131 stems/ha) tree individuals were recorded in the first tree census (2007-2008), belonging to 144 species, 88 genera, and 46 families (Table 1). The total basal area was 869.31 m2 (34.77 m2/ha). Except for two gymnosperms (Podocarpus nakaii and Pinus morrisonicola) and 1 monocotyledon (Arecae catechu), the rest of the woody species were all dicotyledons. In total, 29 species are endemic to Taiwan, for instance, Helicia rengetiensis and P. nakaii. In Taiwan's vegetation classification scheme, the forest belongs to the Machilus-Castanopsis zonation of broad-leaved forests in Taiwan.

The Lienhuachih forest dynamics plot located at west of the Lienhuachih research center.
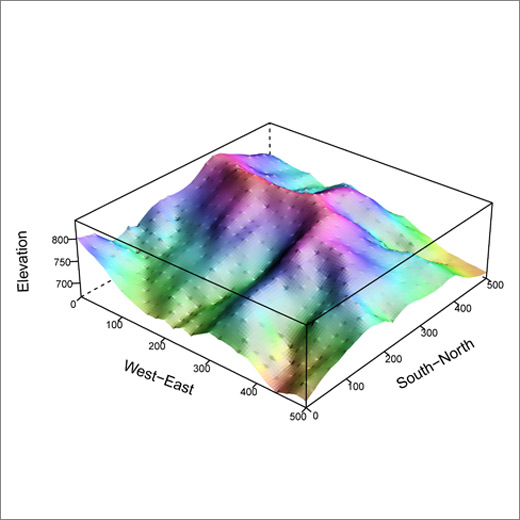
The three-dimentional maps of the Lienhuachih forest dynamics plot.
Plot Data
The field teams measured all horizontal points at 20-m intervals within the 25-ha plot. The plot was divided into 625 quadrats of 20 m ×20 m, each with other subsidiary points at 10-m intervals. Each 20 m×20 m quadrat was further divided into 16 subquadrats of 5 m×5 m. All freestanding trees ≥ 1 cm in diameter at breast height (DBH) were mapped, measured, identified, and tagged.
Data from the tree census and topography survey of the Lienhuachih FDP are accessible. The content of data includes:
- Tree census: The tag number, species identity, diameter size, census date, and location of all woody individuals with at least 1 cm diameter at breast height.
- Topography survey: The survey data (x, y, z coordinates) of 676 stake points within the plot.
Applicants should contact Dr. Li-Wan Chang (EMail:liwanc@tfri.gov.tw ) or Mr. Sheng-Hsin Su (EMail:sush@tfri.gov.tw ) for further information.
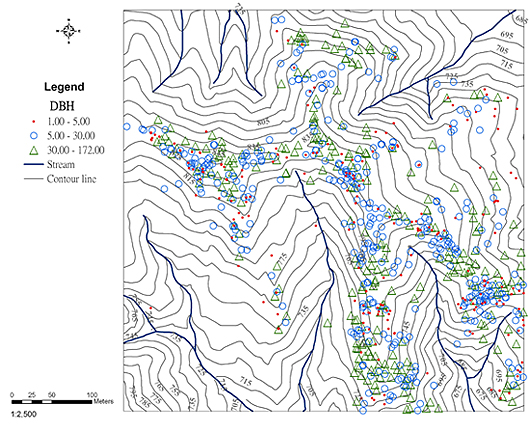
Distribution map of the different size of DBH of Lithocarpus nantoensis in the Lienhuachih forest dynamics plot.
Researchers
- Dr. Li-Wan Chang, Taiwan Forestry Research Institute (plant ecology)
- Pei-Hsuan Lee, Taiwan Forestry Research Institute (plant ecology, fern phenology)
- Dr. Jeen-Lian Hwong, Taiwan Forestry Research Institute (hydrologic characteristics of watershed)
- Prof. I-Fang Sun, National Dong Hwa University (seed rain, seedling dynamics)
- Teng-He Huang, Tunghai University (seed rain, seedling dynamics)
- Prof. Kuoh-Cheng Yang, Providence University (plant Taxonomy)
- Prof. Zueng-Sang Chen, National Taiwan University (soil science)
Partners
Forestry Bureau, Council of Agriculture
����